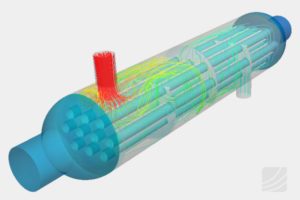
Porous media approach in CFD analysis
Porous Media Approach in CFD Analysis
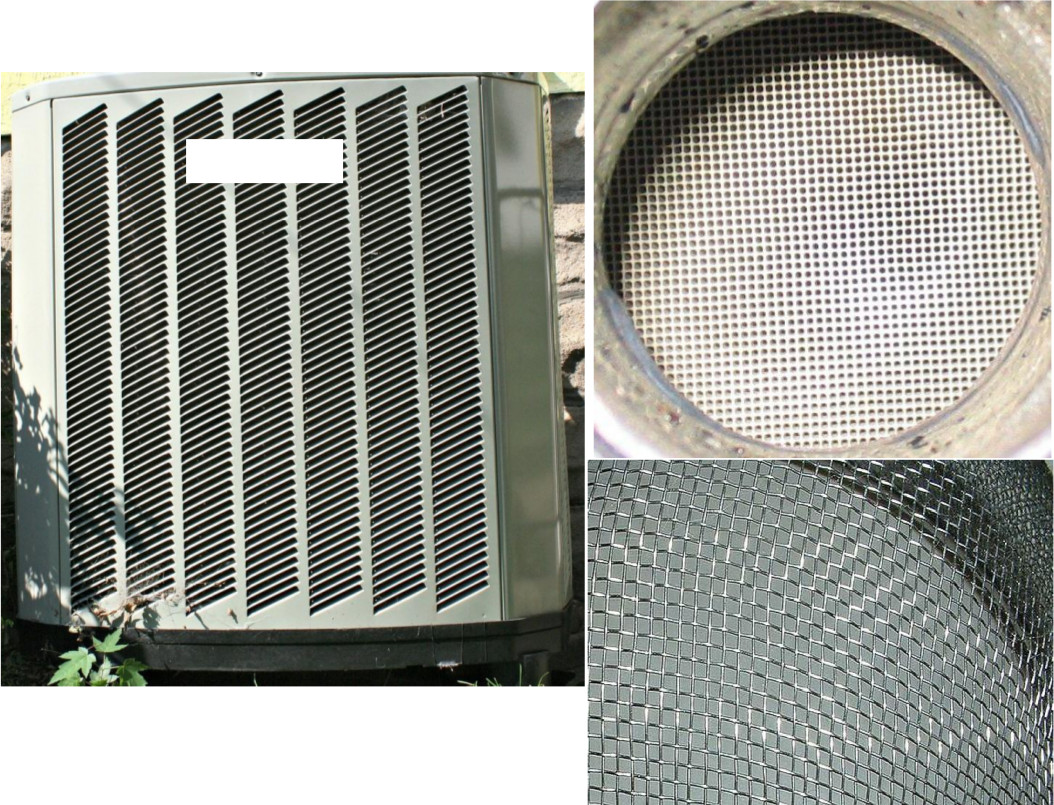
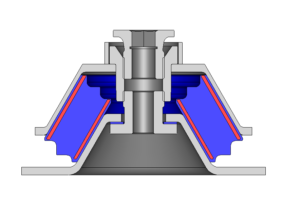
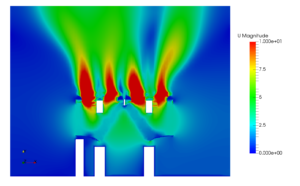
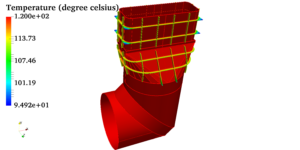
Radiators, filters or catalytic converters have very closely spaced flow paths. It can be said flow will be through pores (small openings). It is practically difficult to extract the flow domain. This is due to closely spaced and thousands of flow paths. Hence in order to solve such problems, the closely spaced flow paths are replaced by a zone having pressure drop information, equivalent to small passages. This is known as porous media approach. There are several ways to represent the head loss in terms of velocity of incoming flow. Darcy-Forchheimer co-relation is one of the methods. Darcy-Forchheimer equation is,
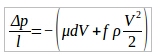
In this equation, the first term is the viscous term via Darcy equation, while the second term is named as the inertial term. The extraction of the porous medium coefficients was obtained by using the unit cell simulations. The coefficients are extracted from the velocity versus pressure plot. Fitting a second order curve to the collected pressure versus velocity data given the Darcy-Forchhimmer relation as,
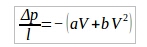
where a and b are the coefficients characterizing the flow. By comparing the above two equations we will get,
Darcy coefficient(d) or Viscous coefficient = a/μ
Forchheimer coefficient(f) or Inertial coefficient =2b/ρ




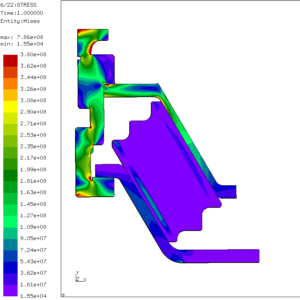
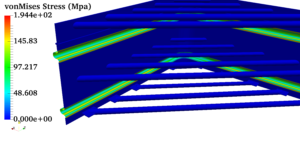
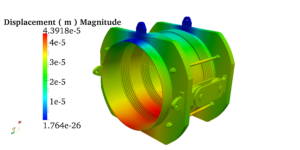
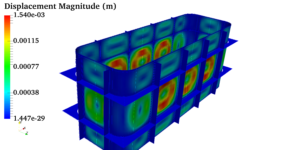 Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.
Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.