Enhancing Cold Storage Design with Computational Fluid Dynamics
Enhancing Cold Storage Design with Computational Fluid Dynamics
Cold storage warehouses are specialized facilities designed for the storage of perishable goods and products that require controlled temperature environments to maintain their quality and freshness. These facilities are equipped with refrigeration systems that allow precise regulation of temperatures. Cold storage warehouses play a critical role in preserving food items,
pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive goods throughout the supply chain. They are essential for extending the shelf life of products, reducing spoilage, and ensuring safe storage conditions until distribution or consumption.
During the operational phase of a cold storage warehouse, maintaining ideal airflow, thermal conditions, and humidity levels is essential for preserving the quality and longevity of perishable goods. The warehouse must ensure efficient air circulation to achieve uniform distribution of cold air across all stored products, preventing temperature variations and maintaining consistent cooling throughout the storage space. Temperature control is critical, with different zones maintained at specific temperatures ranging from chilled storage (generally, 2°C to 8°C) for fruits and vegetables to frozen storage (generally, -18°C to -25°C) for items like meat and seafood. Humidity levels are carefully regulated to prevent moisture-related issues, with chilled storage areas typically kept at a relative humidity (RH) of 85% to 95% to preserve freshness, while frozen storage areas maintain lower RH levels (around 85% or less) to minimize frost buildup and maintain product quality. Efficient energy management practices, regular maintenance of refrigeration systems, and compliance with food safety standards ensure optimal operational conditions and product integrity throughout the cold storage facility’s operations.
Some of the challenges in design of a cold storage warehouse are:
- Uneven airflow distribution
- Undesirable temperature increase/variation
- Condensation
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) offers solutions by simulating airflow patterns and heat transfer, optimizing ventilation and insulation strategies, and evaluating energy-saving measures to enhance temperature control, energy efficiency, and product safety in cold storage environments.
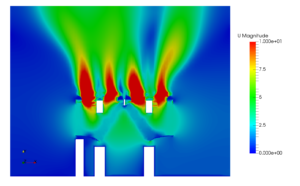
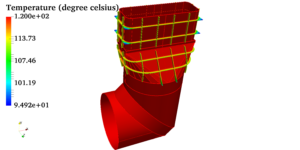
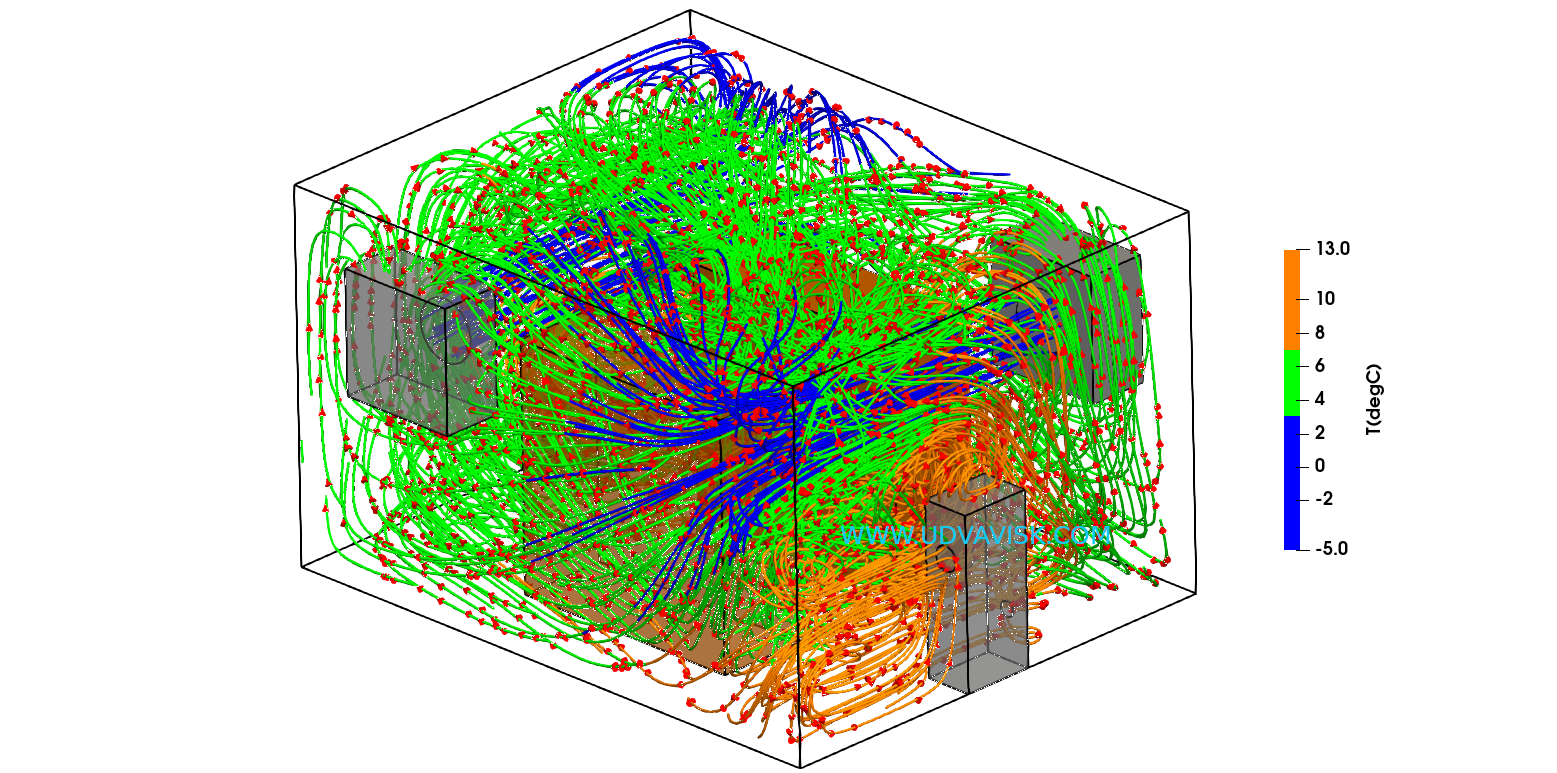
The cold storage warehouses can be virtually simulated to predict the airflow pattern as shown in the below streamline plot (coloured by temperature).
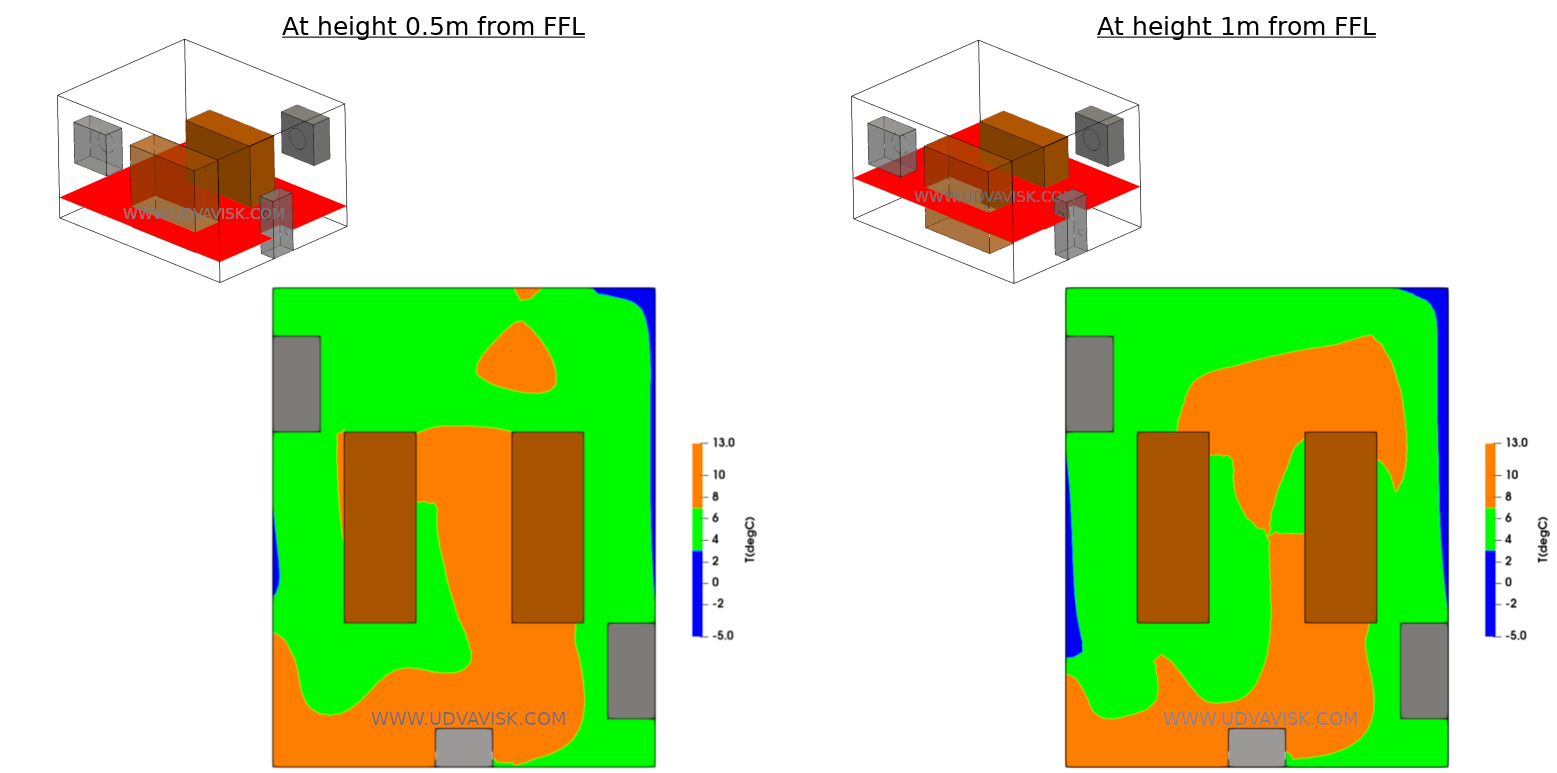
The hotspots (regions of undesirable temperatures) can be identified as shown in the below temperature contours (Blue – cold spots | Orange – Hot spots).
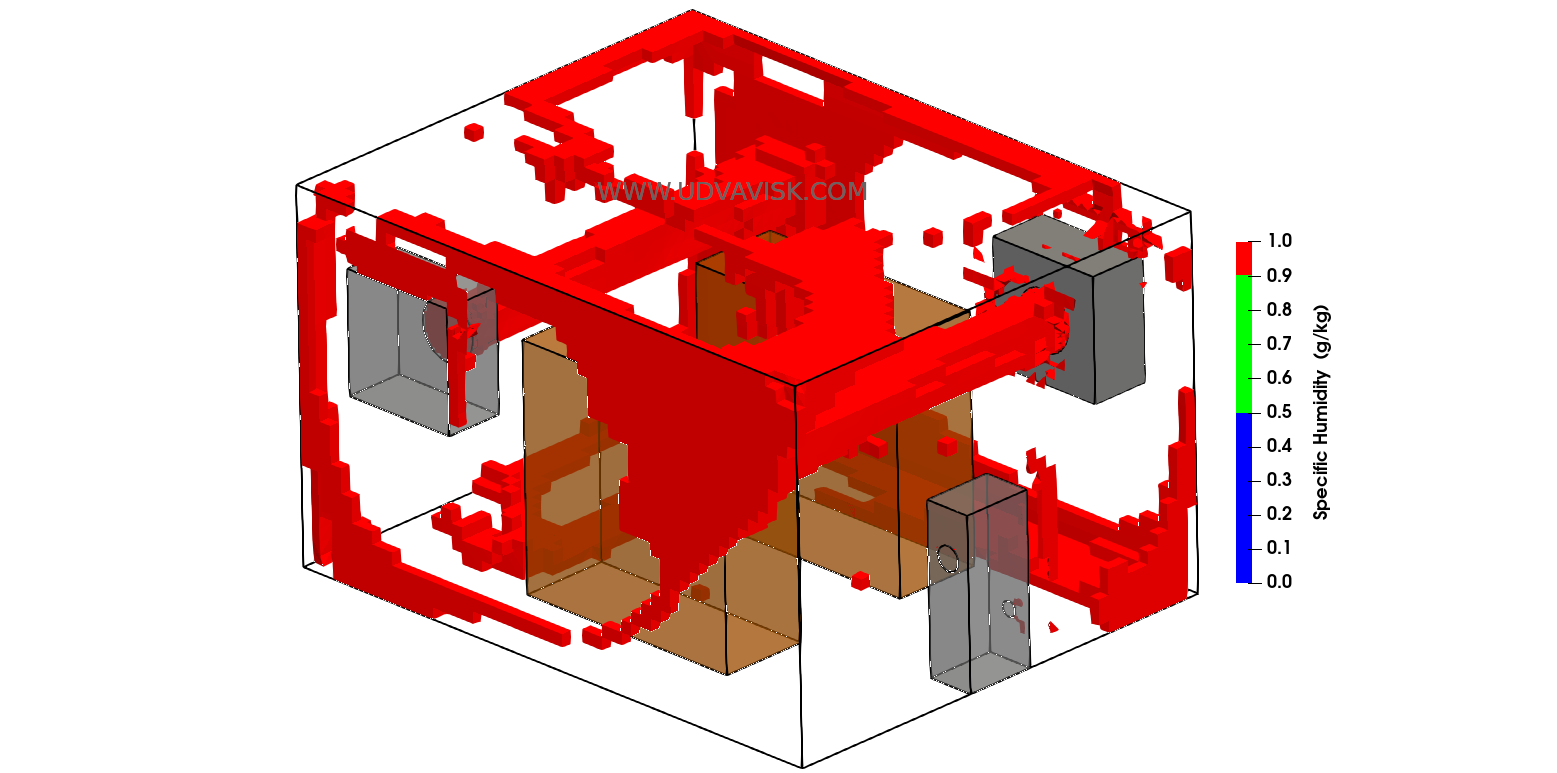
Also, the regions where condensation can be expected within the storage space can also be identified as in the below threshold plot (high humidity regions).
In conclusion, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is instrumental in designing cold storage warehouses by simulating airflow patterns and temperature distributions. CFD helps optimize airflow distribution to eliminate hot spots and cold zones, ensuring uniform cooling throughout the facility. CFD also helps in evaluating insulation effectiveness, optimizing refrigeration system design, and assessing energy efficiency by virtually testing different configurations. CFDvalidates thermal anagement strategies and enables the design of more energy-efficient and reliable cold storage facilities tailored to the specific needs of temperature-sensitive goods.




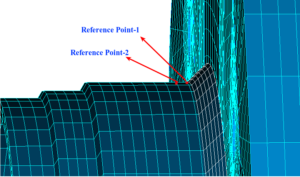
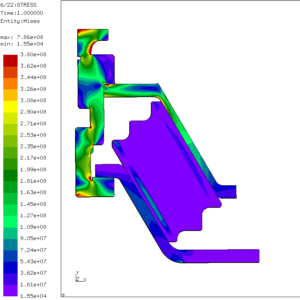
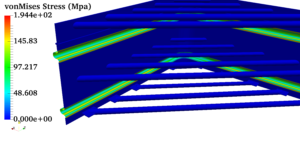
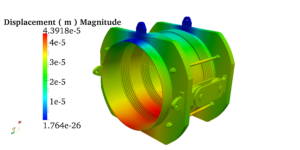
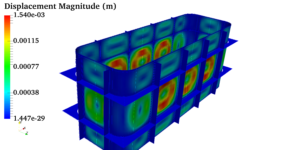 Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.
Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.