Dynamic thermal modeling of warehouse
Dynamic Thermal Modeling of Warehouse
Warehouses spread over a large area have higher energy consumption. The biggest portion of the energy consumption is due to the HVAC systems. ASHRAE recommendations based HVAC system designs can be improved based on hourly energy needs. Weather conditions affect solar heat gains and infiltration loads. Nearby structures may cast shadow on the facility, blocking daylights and corresponding heat gains. Material chosen for building construction will have an impact on conductive heat gains through walls and windows.
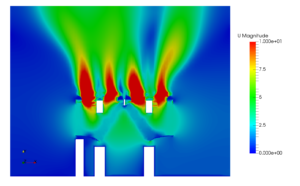
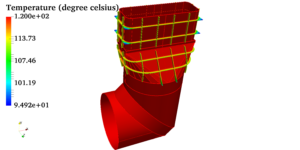
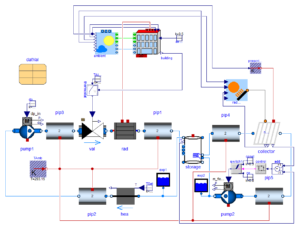
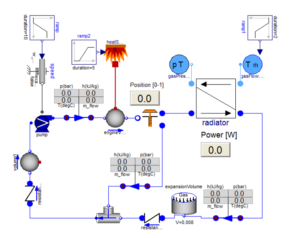
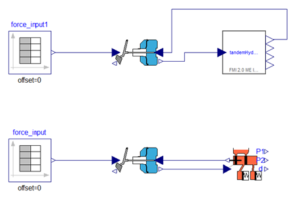
Dynamic thermal load modeling is mathematically finding out the variation in indoor air conditions with continuously varying weather. This modeling relies on numerical techniques for solving simplified model equations. Facilities can have single or multiple thermal zones. Different thermal zones will have different type of heat gains. Some zones will have more occupant loads during a certain period of the day and other zones might have more equipment loads and lighting loads. Some zones in facilities like clean rooms may require more air flow rates. Loads will also have scheduling attached with them. Similarly zonal infiltration load which varies with wind conditions and leakage areas can be estimated sufficiently accurate. Based on all those inputs, energy consumption in the building can be estimated. The effectiveness of existing HVAC system can be determined on hourly basis all round the year by finding zone temperatures and humidity.
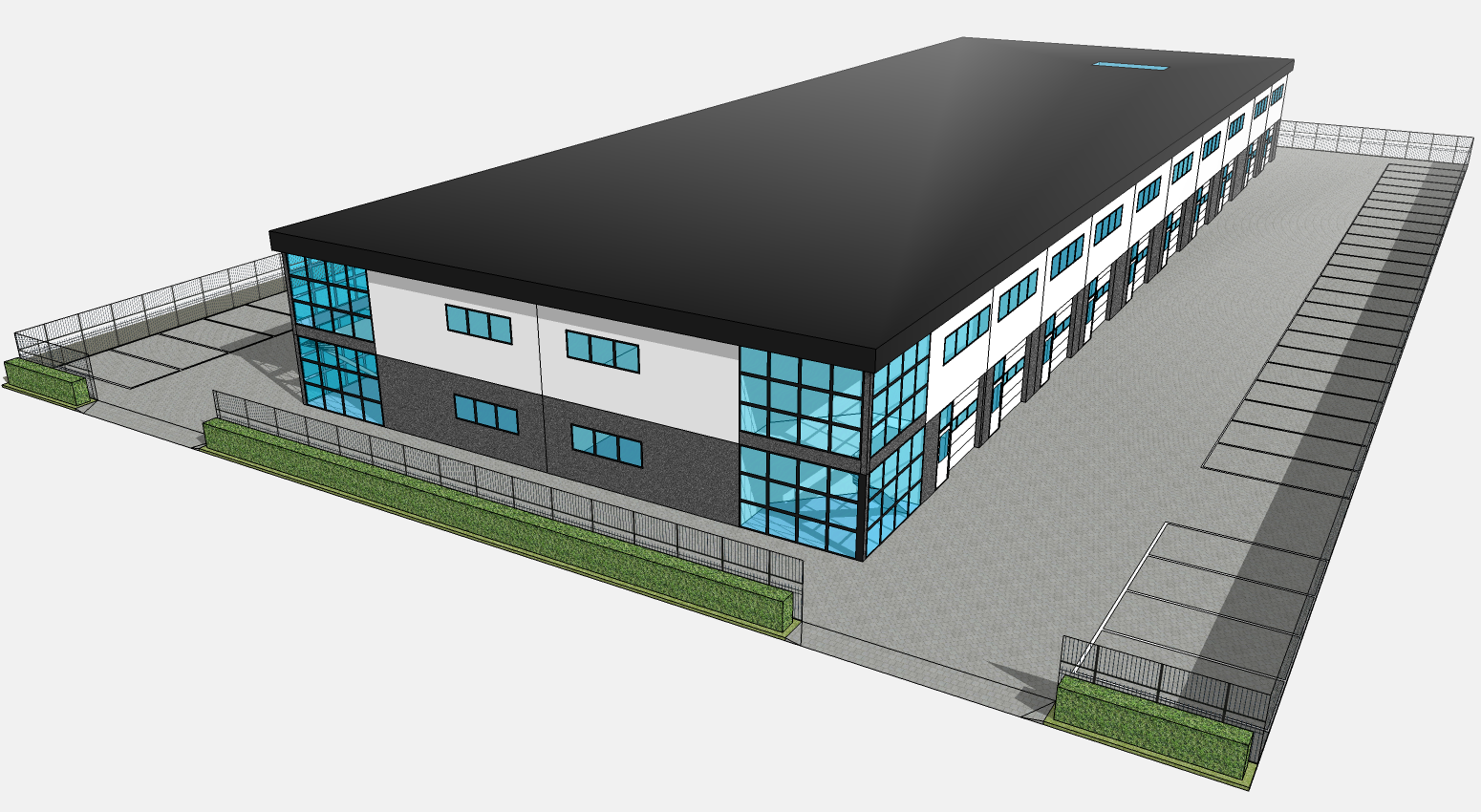
A furniture warehouse at Riyadh is considered for this study. Riyadh is located at 612 m above the mean sea level. It has a climatic condition of high temperature extremes with prevalent dry desert conditions. The proposed facility is spread over 1.7 lakh ft2. A large surface area is exposed to the sun due to high roofs. The HVAC systems are in place to take account of 50 occupants during working hours from 8:00 am to 5:00 pm. Lighting, solar transmissions, sky light and infiltration loads are considered for generating hour-wise zone temperature. The HVAC system is having a cooling coil, a cooling set point manager, a heating coil, a heating set point manager, humidifier and supply fan. The construction set is based on recommended material for climate zone 2a.
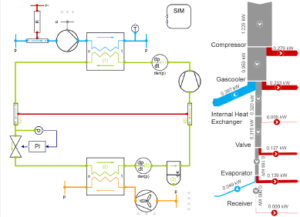
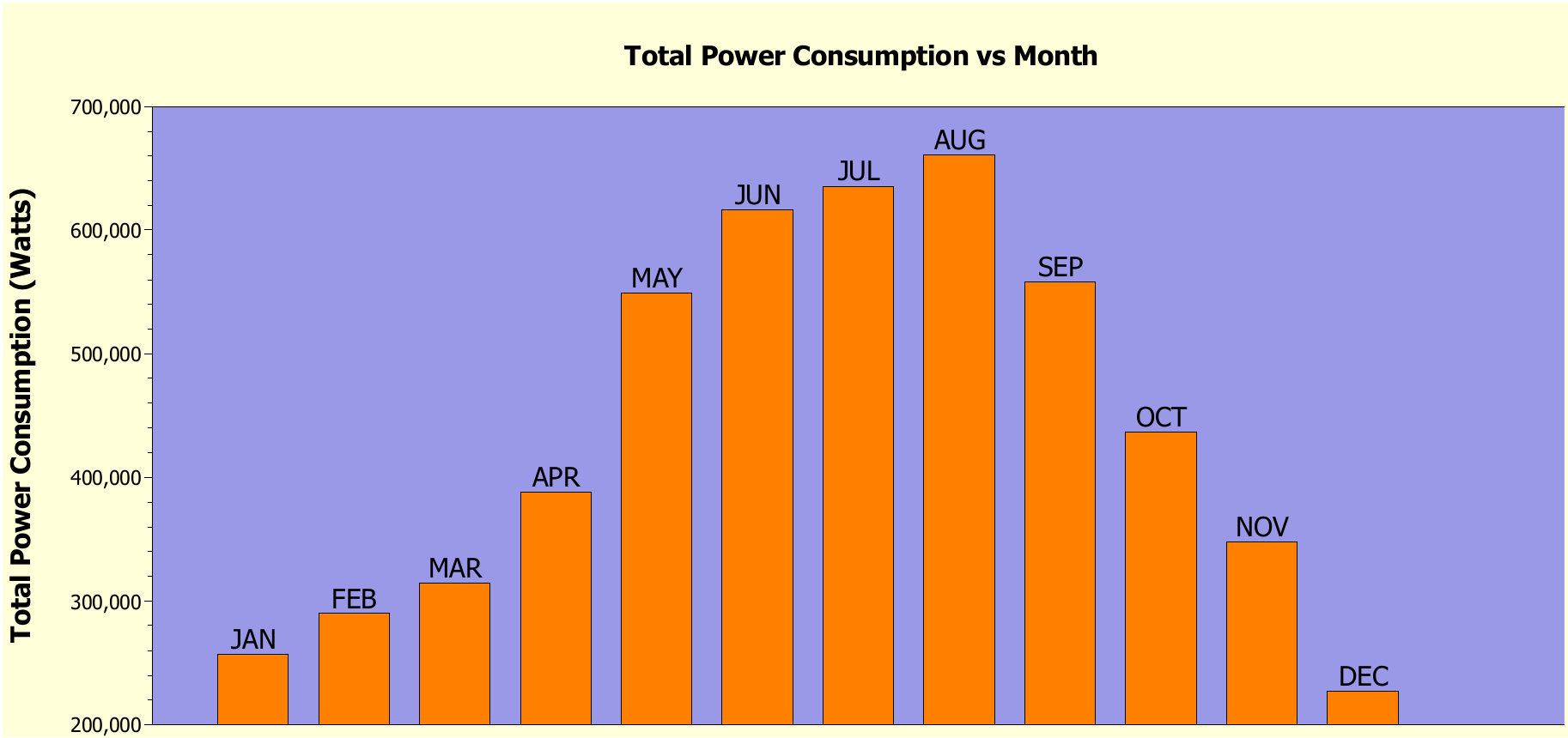
The energy budget estimation for the facility is represented in the picture. It can be observed that during August month energy consumption is maximum and in December it is minimum. Energy consumption is due to the fork lifts in the warehouse, lighting in the warehouse and also load due to HVAC system equipment’s such as cooling coil, supply and dehumidifiers. The energy budget of the facility can be improved based on recommendations on green buildings.


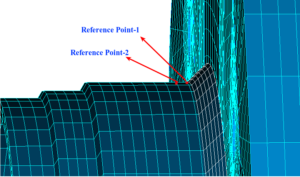
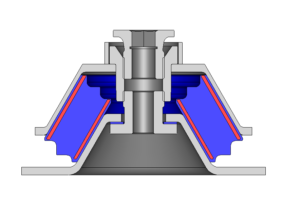
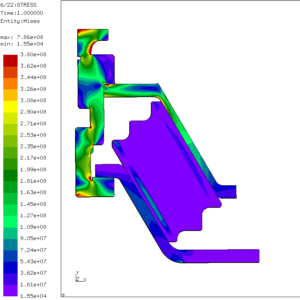
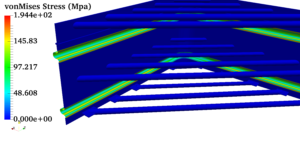
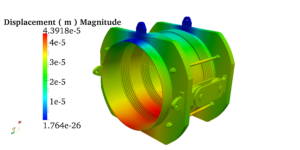
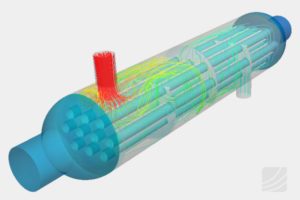
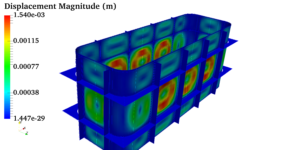 Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.
Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.