CFD analysis of clean rooms for contamination tracking
CFD Analysis of Clean Rooms for Contamination Tracking
Clean rooms or sterile facilities are maintained under a conditioned space. Several engineering fields such as the aerospace industry, the semiconductor industry, hospitals and pharmaceuticals need to maintain clean-rooms.. Clean rooms are spaces where the concentration of unwanted foreign particles and environmental conditions must be maintained in a stringent manner. For instance, the presence of impurities are not acceptable for a semiconductor based product as it may severely affect the performance of the product. Similarly, pharmaceutical drugs manufactured for health related issues and environmental purposes will be considered as adulterated if the concentration of the foreign agents which are present in the substance is beyond an acceptable limit.
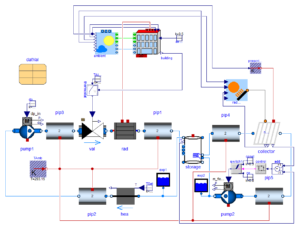
In this study is to estimate the concentration of contaminants per cubic volume of air in a pharmaceutical facility and the efficiency of the HVAC system installed to tackle the particulates. There are several classes of clean rooms depending on the concentration of particles present in a space. Moreover, designation of classes is also a function of the particulate diameter which is being generated. The ISO standard 14644 recommends an acceptable practice which is followed with rigour in most parts of the world. The recommendations in the standard are usually based on experiments and several research activities. They are tentative and subject to minor changes during every course of time. It is always better for a HVAC designer to keep oneself updated with respect to the standards.
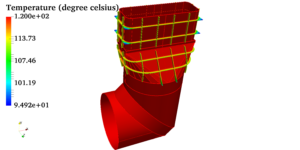
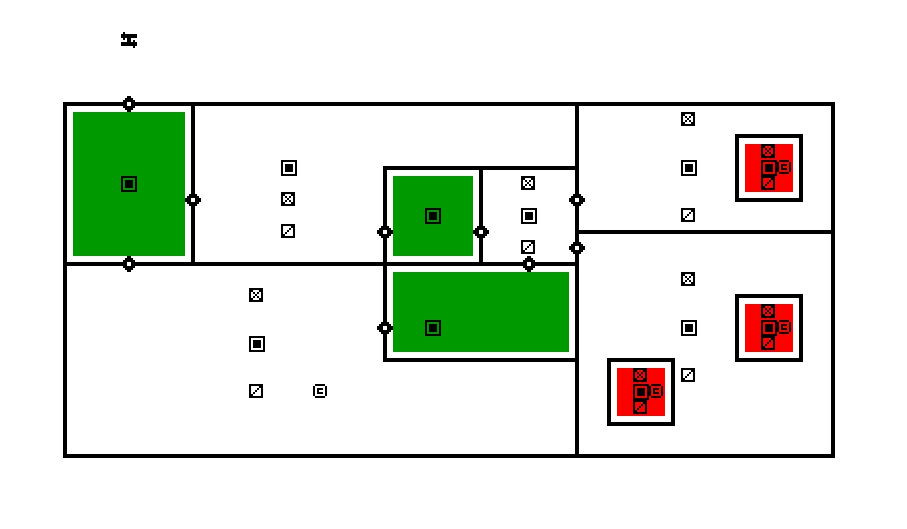
The facility which is under study in this case consists of airlocks, which are indicated by dark green color. Airlocks are zones which are used to facilitate a differential pressure between two zones of different cleanliness. They are highly ventilated zones where the airborne particle quantity must be as same the quantity of particles in clean zones at a state of rest. There are four types of Airlocks generally employed in the industry depending on the direction of flow. The facility also contains critical areas marked in red, which are the filling rooms where the product is filled in vials. The concentration of hazards must be maintained at a very low level in these zones to avoid adulteration of drugs. Apart from these zones the facility also contains autoclave loading zone, and a zone for washing and sterilizing equipment. To study and simulate a very realistic scenario the critical areas were assumed to be class five clean zones where the permissible level of particle concentration is three thousand two hundred and fifty per cubic volume of air. Hence a source of contaminant producing 3E-8 microgram per second of particles with a diameter of 0.5 micrometer is used. Strictly conferring to ASHRAE Applications handbook, based on the recommended velocity and Zone heights an appropriate Air handling system was selected to operate in the critical areas and a HEPA filter with an efficiency of 0.9997 was chosen to operate at the supply outlet.
Results:
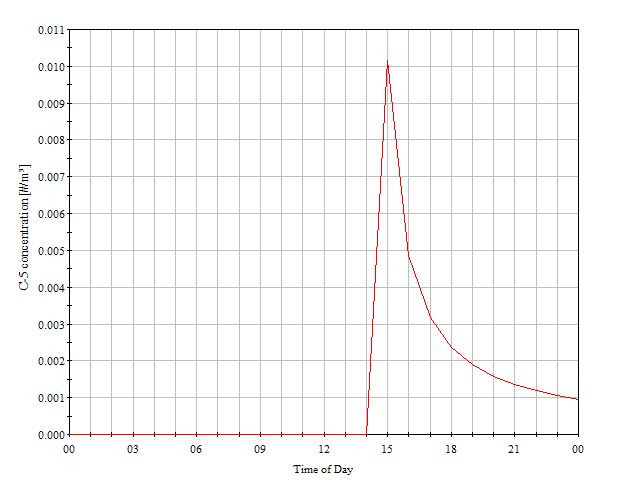
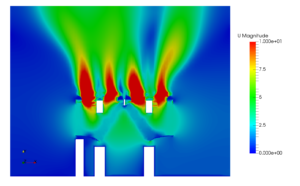
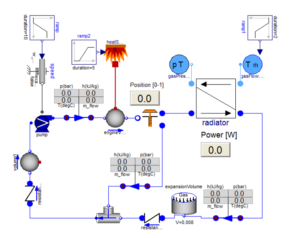
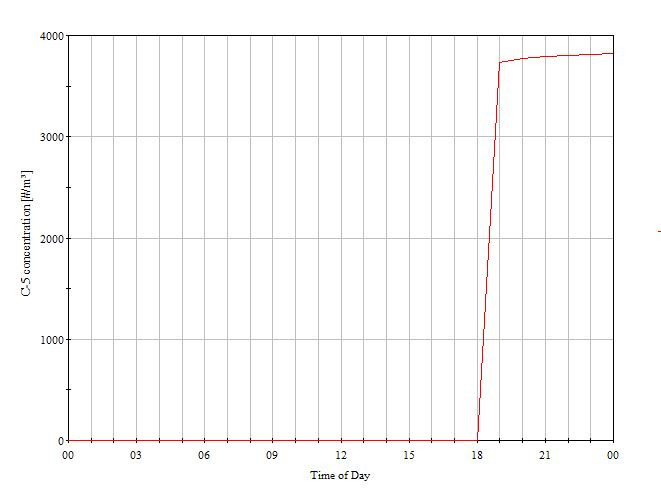
The entire case was simulated for a design day and the concentration of airborne particles was found to be well within the acceptable range. Along with that, an additional case was simulated by considering the failure of the Air handling unit as a part of disaster management study to estimate the magnitude of catastrophe which will occur or the amount of particles which will be generated in case of a AHU failure.




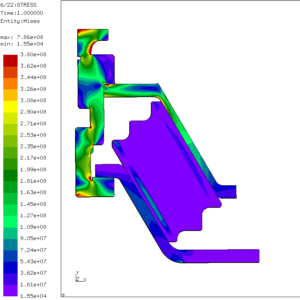
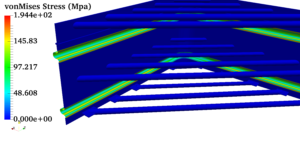
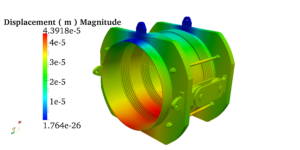
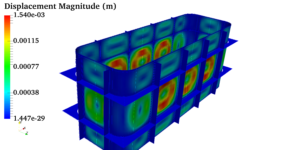 Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.
Pressure vessels, pipes, expansion joints etc. are basic equipments for process industries. Pressure vessels are vessels working under internal, external or vacuum pressure, and possibly subjected to high temperature. Proper design and analysis is very important for the pressure vessels, as their failure can cause lot of hazards. Codes/ standards are used in the design phase, followed by analysis to ascertain stresses are within the allowable range. ASME provides wide range of guidelines for the proper design of such vessels.